



With the explosive development and accelerated iteration of artificial intelligence (AI), its application in clinical trials is also constantly deepening. By analyzing external data to provide precise decision-making insights, AI can help improve the quality and efficiency of clinical trials. Medidata, a brand under Dassault Systemes, provides analysis and AI solutions for the life sciences industry, helping sponsors answer the core question of all clinical trials: why patients choose to use their drugs. For example, in the development of cancer drugs, signals based on early stages of cancer treatment can verify the potential efficacy and long-lasting, positive clinical benefits of drugs for patients.
In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced accelerated approval of the first CAR-T cell therapy developed by BMS for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (R/R CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) - Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel; liso cel). This breakthrough achievement has opened up a new treatment option for patients who have received dual line therapy including BTK inhibitors and BCL-2 inhibitors.
In the context of limited existing treatment options and strict regulatory requirements for the quality and analysis methods of alternative endpoint data, Medidata relied on its massive and accurate patient level historical trial dataset and innovative AI comparison model to optimize the trial plan for Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) and provide critical evidence for its FDA approval acceleration, effectively accelerating the process from trial to market.
The feasibility of traditional experimental schemes is low, and the difficulty of experiments is doubled
CLL and SLL are common leukemia in adults, typically characterized by abnormalities in lymphocytes in the blood, bones, or lymph nodes. This type of disease progresses slowly, and most patients need to cope with it for a long time, but treatment is difficult. If traditional indicators are used as endpoints in the trial, it requires years of follow-up, which is time-consuming and laborious; At the same time, patients urgently need effective therapies, and waiting for traditional indicator results for a long time will further delay treatment opportunities for more patients and make recruitment for trials difficult. After comprehensive evaluation, BMS believes that alternative endpoints may be the key to breaking the deadlock - by using complete response (CR)/partial complete response (CRi) within one year after treatment as alternative endpoints for progression free survival (PFS), in order to obtain FDA approval for accelerated marketing.
However, although the FDA recognizes the experimental design of BMS, it requires BMS to provide strong clinical validation and statistical evidence. To comply with the FDA's strict review criteria for alternative endpoints, BMS not only needs to demonstrate a clear association between CR/CRi and long-term patient survival, but also needs to demonstrate that the data used is valid comparative data.
Exploring the potential of experimental data, artificial intelligence may be the key to breaking the deadlock
Usually, to demonstrate whether a certain alternative endpoint is applicable to a certain mechanism of action of a novel drug, historical data can be used to verify that its short-term treatment response is generally associated with long-term survival and is applicable to any mechanism of action.
BMS requires reliable external data for effective clinical comparative validation, to complete its' statistical evidence '. BMS has entrusted this important task to Medidata.
Medidata's data accumulation gathers over 36000 clinical trials covering different disease domains and mechanisms of action, as well as historical trials involving over 11 million patients, making us one of the best sources of evidence for conducting such research. From the historical data of many different mechanisms of action, we see a strong correlation between short-term treatment response and long-term survival, so we have reason to believe that regulatory agencies will agree to apply this correlation to new mechanisms of action.
Based on the goal of BMS, Medidata has compiled a dataset of over 5 historical clinical trials, including data from more than 1600 relapsed/refractory CLL/SLL patients who have previously received at least one treatment regimen (BTKi, BCL2i, PI3K, or anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody). At the same time, a time event analysis was conducted to evaluate the relationship between achieving and maintaining CR/Cr at 12 months after treatment and the long-term survival of patients.
Based on the above historical dataset, Medidata built a comparative model for BMS within a few weeks and provided BMS with the results of the comparative analysis of prognostic factors and post-treatment response data to support the scheduling of its clinical trials and regulatory meetings.
Among all patients, the CR/CRi ratio was 15.08%. According to the Landmark analysis method to control for time bias, Medidata comparison data demonstrated a significant correlation between achieving and maintaining CR/CRi within 12 months after treatment and improving long-term survival outcomes. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) was 0.62 (95% confidence interval: 0.42-0.90, p-value=0.01). At the same time, compared with patients who only achieved partial remission (PR) or no remission at all (nPR), patients with recurrent or refractory CLL/SLL who maintained CR/CRi after treatment had a more significant survival advantage, and were superior to patients who did not achieve any remission or were unable to maintain it after switching (as shown in the figure below).
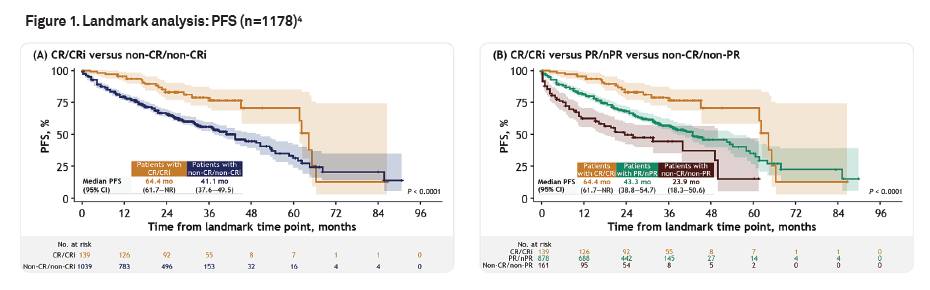
The results showed that CR/Cr response within 12 months after treatment can be an early response endpoint for evaluating progression free survival in the patient population. This provides basic evidence for BMS to apply for accelerated approval to the FDA, making it the first FDA approval for CAR-T therapy in CLL/SLL patients.
The above experimental evidence, as well as other evidence provided by BMS, has advanced the market launch of the drug by several years. Relying on Medidata's AI solution, we have successfully helped this outstanding innovative drug to reach the market faster and benefit patients.
The successful case of BMS has the potential to completely change the design of cancer clinical trials, shorten trial time, and save development costs. It also further proves the value of powerful and robust AI intelligence tools in clinical research and development, as well as their potential to empower innovative drug research.
Chen Beini/Wen
[?1]
[?2]
American Cancer Society. Cancer Faots & Figures 2022.
[?3]
Typical Treatment of Chronic Lymphooytic Leukemia. Accessed January 8, 2025. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/chronic-lymphocytic-leukemia/treating.html

Subsidy policy shifts, car market sales decline for three consecutive months

HSBC reports that gold prices may hit the $5000 mark in the first half of the year, with market expectations that silver prices will continue to rise

How can Herm ? s in the mobile phone case industry make young people rush to buy it?
